(Correspondent Jiankun Guan) On October 9th, a research paper entitled "A novel prodrug and its nanoformulation suppress cancer stem cells by inducing immunogenic cell death and inhibiting indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase" has been published on Biomaterials (IF=12.479), which proposed a novel strategy to eliminate cancer stem cells via remodeling cancer stem cells niche, and reported a novel prodrug and its nanoformulation. This work is contributed by the team of Prof. Zifu Li and Prof. Xiangliang Yang from College of Life Science & Technology and National Engineering Research Center for Nanomedicine, HUST.
Malignant tumors have become the first cause of death among Chinese residents. One of the key obstacles hindering clinical treatment of malignant tumors is cancer stem cells (CSCs). A large number of clinical data indicate that there are abundant CSCs in varies types of cancer. Traditional chemotherapeutic drugs not only cannot effectively kill CSCs, but also increase the proportion of CSCs and lead CSCs into dormancy. Besides, the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment creates a favorable niche for CSCs via a variety of signaling pathways mediated by the immunosuppressive cells, the highly expressed enzymes, and immunosuppressive cytokines. How to effectively eliminate CSCs is an important issue that urgently needs to be resolved in clinical cancer treatment.
According to the background mentioned above, in this study, a novel strategy to eliminate CSCs via remodeling CSCs niche was proposed. On the one hand, chemotherapeutic agents induced ICD responses would promote DC maturation and elicit robust antitumor immune responses. On the other hand, IDO inhibition would abolish the suppressive tumor microenvironment mediated by Treg cells, amino acids, and cytokines. Both of these two sides contribute to regulating CSCs niche and potent antitumor efficacy in TNBC. These together relieved the cell cycle arrest of CSCs, and made CSCs more vulnerable to antitumor immune cells and chemotherapy drugs, contributing to potent elimination of CSCs. Based on this strategy, a novel prodrug and its nanoformulation were successfully designed and fabricated, which showed significant better antitumor efficiency in triple-negative breast cancer model than the clinical first-line drugs paclitaxel and irinotecan.
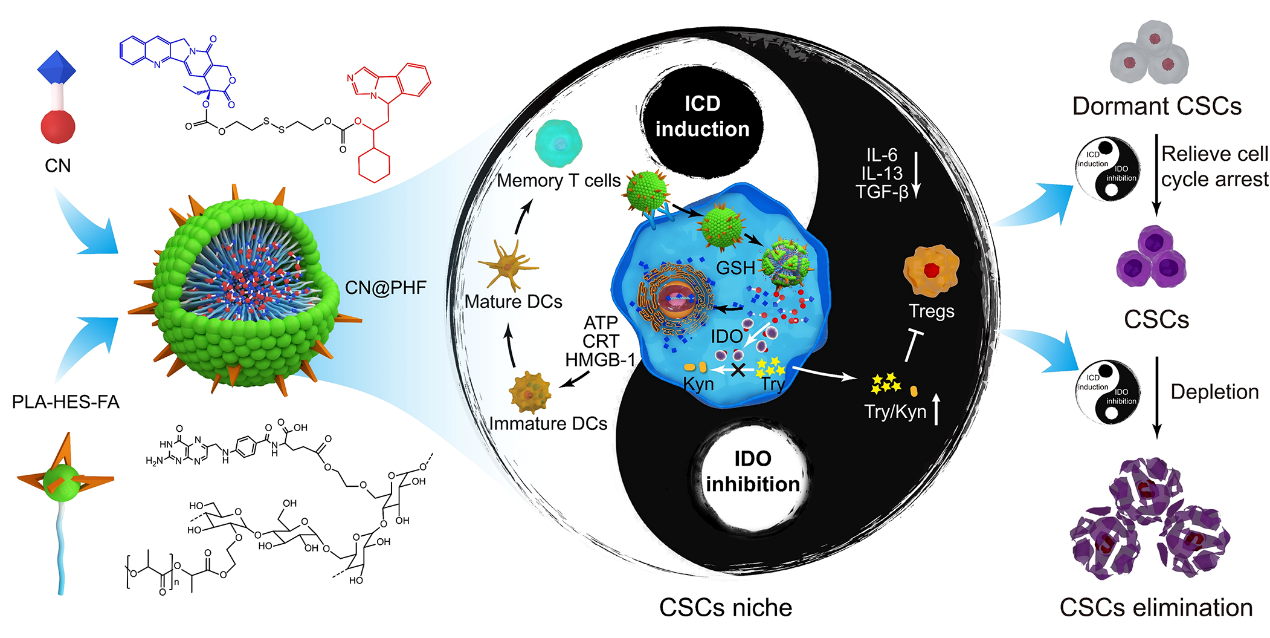
This study proposed a novel strategy to relieve CSCs dormancy and eliminate CSCs via remodeling CSCs niche by the combination of inducing immunogenic cell death and inhibiting indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase, which has important implications for anti-CSCs therapy. This study systematically evaluated the antitumor activity, toxicity and optimal dosage of prodrug molecule CN and its nano-preparation. The prodrug molecule CN and its nanoformulation showed great potential for bedside applications.
Ph.D. candidate Jiankun Guan, master student Yuxin Wu and post-doctor fellow Dr. Xin Liu, from College of Life Science & Technology, HUST contributed equally to this work. This work was financially supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFA0211200, 2020YFA0710700, and 2018YFA0208900), the National Science Foundation of China (31972927), the Scientific Research Foundation of HUST (3004170130), the Program for HUST Academic Frontier Youth Team (2018QYTD01), and the HCP Program for HUST.
Article Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142961221005378