我院朱斌教授最近在Frontiers in Microbiology发表的研究论文“Klebsiella Phage KP34 RNA Polymerase and Its Use in RNA Synthesis”于6月3日被列为世界学术组织“Faculty Opinions (原F1000Prime)”推荐论文,并由俄亥俄州立大学Venkat Gopalan教授进行点评。
Faculty Opinions (原F1000Prime,于2020年4月12日改名为Faculty Opinions)是国际生物医学领域重要的学术论文评估机构,由全球近8000名生物学和医学领域的顶尖科学家组成。“Faculty Opinions”中的科学家从每年所发表的生物医学论文中评选出一小部分(不足千分之二)最重要的文章,推荐给全世界的生物学和医学工作者,并对论文加以评论。研究论文能被Faculty Opinions点评与收录,代表着该论文有较高的学术水平和重要的科学价值。
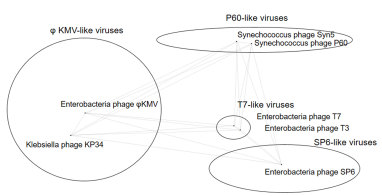
评论明确指出了朱斌教授课题组的特色研究方向“自然界新颖噬菌体单亚基RNA聚合酶的发现和应用”对整个RNA研究领域的重要性。长链RNA的体外合成工具酶数十年来为T7和SP6类噬菌体的单亚基RNA聚合酶所垄断,工具酶的匮乏以及现有工具酶的缺陷成为领域发展的瓶颈。而近年来新发现的可能含有单亚基RNA聚合酶的两个噬菌体家族则提供了革新RNA体外合成工具的潜力。2013年起朱斌教授主导了P60类海洋噬菌体首个单亚基RNA聚合酶Syn5的研究和开发,本次被推荐和评论的工作则是关于已知的最后一类可能编码单亚基RNA聚合酶的噬菌体家族-phiKMV家族的首个代表性RNA聚合酶-KP34 RNA聚合酶的发现和鉴定。KP34 RNA聚合酶与已知所有噬菌体RNA聚合酶差异较大,表现在它是唯一一个能识别两类毫无相关性的强弱转录启动子的单亚基RNA聚合酶。在RNA合成应用方面,KP34 RNA聚合酶能克服T7 RNA聚合酶在合成尾部含有二级结构的RNA时发生额外延伸的缺点,更适合精准合成这类RNA(包括最近常用的基因编辑sgRNA)。
华中科技大学生命学院朱斌教授为通讯作者,博士研究生陆雪玲为该论文的第一作者。
评论原文如下:
RNA biology research has advanced rapidly in part due to phage-encoded single-subunit RNA polymerases (ssRNAPs) that are routinely used for RNA synthesis by run-off in vitrotranscription (IVT). All ssRNAPs (i.e., T7, T3, SP6, and Syn5) currently used in IVTs are derived from bacteriophages in three out of the four clusters of the Autographivirinae subfamily. Now, Lu et al. have characterized Klebsiella phage KP34 RNAP, the first representative ssRNAP from the fourth cluster that houses the phiKMV-like viruses. The locus encoding this ssRNAP is located between the DNA metabolism and structural genes, a genomic feature that differentiates this cluster from the other three in which the ssRNAP gene is located upstream of the DNA metabolism genes. To establish KP34 RNAP for use in IVTs, the authors identified the promoter sequences and optimized the reaction conditions with respect to temperature, pH, and salt concentration. Interestingly, RNA-Seq analysis of the products generated by KP34 RNAP revealed that this enzyme does not produce self-templated 3’ extensions like the widely used T7 RNAP, even with a sequence that is prone to foldback. Instead, KP34 RNAP products tend to have 3’ ends that are either full-length or shorter by 1-3 nucleotides. This important finding of KP34 RNAP’s decreased self-templated 3′-extension activity as well as fidelity considerations needs to be further characterized using a suite of templates and complementary analytical methods. Regardless, this study highlights the value of investigating novel ssRNAPs, especially by leveraging the surge in viromes, to identify natural variants that could foster innovations in RNA biology.
论文链接:
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02487/full
评论链接:
10.3410/f.736931268.793574829